1 -1 -1
y = 1/sin (x) or ------- or sin (x) or sin (x)
sin x
-1
Oops
! This is wrong as sin (x) is arcsin (x), which is the
inverse (not reciprocal ) of sine function.
First reciprocal of sine function.
y = sin (x) is very familiar
sin (0) = 0
sin
(π/4) = 1/√2
sin
(π/2) = 1
sin
(π3/4) = 1/√2
sin
(π) = 0
sin
(π5/4) = - 1/√2
sin
(π3/2) = -1
sin
(π7/4) = - √2
sin
(2π) = 0
Therefore
the reciprocals are
1/sin
(0) = ?
1/sin
(π/4) = √2
1/sin
(π/2) = 1
1/sin
(π3/4) = √2
1/sin
(π) = ?
1/sin
(π5/4) = - √2
1/
sin (π3/2) = -1
1/sin
(π7/4) = - √2
1/
sin (2π ) = ?
<?> is a big <?> as you will see soon.
<?> is a big <?> as you will see soon.
1
As
the sin x is the denominator ------, when sin x approaches 0, the
value becomes + ∞
sin x
sin x
or - ∞ . This is strange. 1/ sin (2π ) = ?
How
about the graph ? <sin x> is
-1 < sin x < +1 or the min value -1.
= =
1
= =
1
As
the sin x is the denominator ------, when sin x approaches 0, the
value becomes + ∞
sin
x
or
- ∞ . This is strange. <sin x> approaches 0 from 1/4 π it goes + ∞ while <sin
x> approaches 0 from -1/4 π approaches it goes - ∞. You
can see this in the following graph. How to interpret or explain
this ?
See
the graph. From Wiki.
1
y = -------
sin x
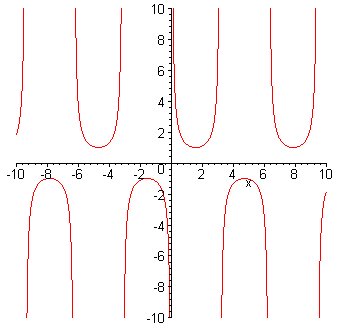
x-
axis is radian. So at x = π/2(3.1415/2 = 1.5706) the value is 1 and
x = π3/2 (3.1415x3/2 = 4.7123) the value is -1.
1
As
sin x is cyclical so is -------.
sin x
-1
Now
try to understand sin (x) or arcsin (x) or a reverse function
of sin (x).
2
y = x
The
reverse function of this is
2
x = y
and then
y
= +/- √x
x
= 0 , y = 0
x
= 1 , y = +/- 1
x
= 2 , y = +/- √2
x
= 4, y = +/- 2
x
= 9, y = +/- 3
From Quora
We already discussed this relation
before in <Function of y =
x>. This is a mirror image
of y = x against y = x so <inverse> function. However 1/ sin x,
though called <inverse>,
is not a mirror image of y = x.
sin (π/4) = 1/√2
-1
while sin (π/4) or arcsin (1/√2) =
π/4
In this sense y = arcsin (x) s called the <reverse>(relation) of y = sin (x).
Confusing but the point is <π/4> of
sin (π/4) = 1/√2 is an angle
(either in degree or in radian, radian is much more convenient) while <1/√2>is a ration <1:√2>of
the two line elements of a right triangle. On the other hand in<arcsin (1/√2) = π/4>
an angle is a calculation result of the the ratio. Thai is
all.
Look at the graph of
y = arcsin (x).
I have found the following article.
-and-arcsin(x).gif)
This graph was made beautifully and shows clearly the function of the line y = x.
ACT
No comments:
Post a Comment